Asian Leopard Cat: Unveiling the Mystery
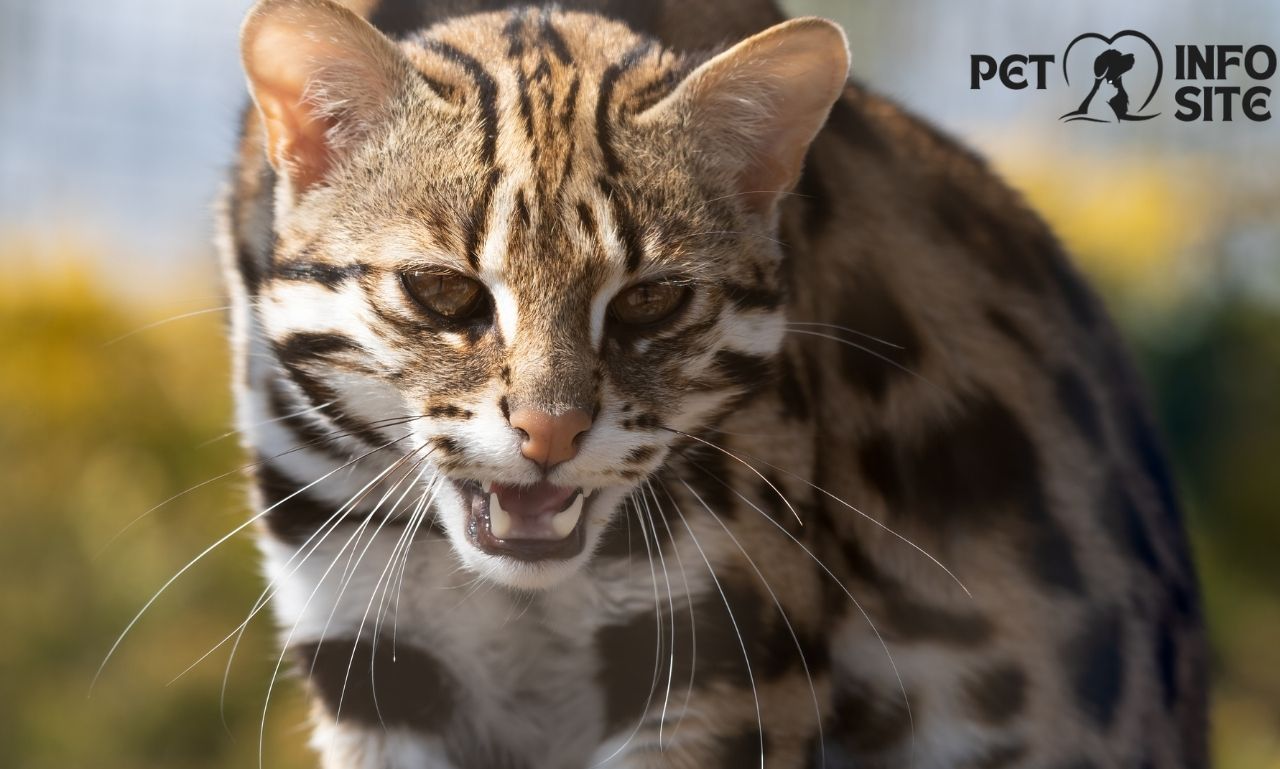
Scientists have accredited the Asian leopard cat with the name Prionailurus bengalensis; this name represents elegance and versatility across Asia’s diverse terrains. Its beautiful and unique coat pattern of brown spots on a tawny background and graceful movements have always fascinated people.
| Leopard Cat | |
| Scientific Name | Prionailurus bengalensis |
| Conservation Status | Least Concern since 2002 |
| Native Regions | South Asia, Southeast Asia, and East Asia |
| Distinct From | Sunda leopard cat (Prionailurus javanensis) |
| Physical Variations | Subspecies differ in fur color, tail length, skull shape, and size of carnassials |
| First Domesticated | In Neolithic China, around 5,000 years ago in Shaanxi and Henan Provinces |
Physical Characteristics: A Closer Look at the Beauty Within
The Asian leopard cat is a slim cat, with an adult weight of 4. 5 – 5 kg. The long legs and thick, ringed tail are the essential adaptions to enable its movements through its natural habitat. The coat displays solid or rosette-shaped spots, colored in hues ranging from reddish-brown to ochre-yellow, reflecting the cat’s geographic diversity.
Habitat and Distribution: Roaming the Diverse Landscapes of Asia
From the Russian Far East to the Indonesian archipelago, these species of Asian leopard cats cover such extensive areas. These creatures inhabit a wide range of environments, from thick tropical rainforests to the rocky foothills of the Himalayas, rather than being confined to a single habitat. Incredible, the cats have been spotted even at a height of 4,500 meters, which shows their ability to adapt to various climates.
Behavior and Adaptations: Surviving in the Wild
Asian leopard cats are highly specialized predators, well-known for their exceptional agility and proficient hunting skills. Being excellent climbers and swimmers, they are capable of hunting prey in water as well as on land. Their diet consists of small mammals, birds, reptiles, and insects, which serve as food for them and thus their role as an apex predator. Their unique coloration helps them to blend in with the dense vegetation, not only facilitating hunting but also helping them to escape from predators.
Conservation Status: A Precarious Existence
While they are resilient, Asian leopard cats are prone to several factors that are threatening their existence. Habitat loss, which is a result of deforestation and human encroachment, is the main cause of population decline in some areas, and hunting for the fur and pet trade is also a reason for the decline in some areas. Although labeled as “Least Concern” by IUCN, they are highly vulnerable in China and the Philippines.
Human Interaction: Threats and Challenges
The encroachment of human activities poses a very big threat to the sustenance of this species. Land deforestation for crop farming and settlement construction reduces their natural habitat, forcing them to live near human settlements. Besides, illegal hunting and trade, these activities increase the severity of the population decrease, which makes conservation efforts even harder.
The Bengal Cat Connection: Domestication Attempts
The attractiveness of the Asian leopard cat’s appearance has provoked its domestication. The Bengal cat, a crossbreed combining the Asian leopard cat and domestic cats, features the wild beauty of the latter. On the other hand, Bengal cats that are inborn in the wild behavior can be quite tricky to live with, leading to the obvious distinction between wild and tamed creatures.
Celebrating the Majesty of the Asian Leopard Cat
To sum up, the Asian leopard cat is the embodiment of nature’s resiliency and the triumph of beauty. Even though this exceptional animal faces a variety of difficulties, it manages to survive in the different ecological zones of Asia. As the planet’s guardians, we should spare no effort to preserve this wildlife. Thus, the conservation of this animal is essential to its long-livedness. Explore more fascinating insights about exotic felines and pet care on Pet Info Site, your ultimate destination for all things furry and fabulous
FAQs
Thus, even though these animals are sylvan, they rarely attack people unless when provoked to do so, such as Asian leopard cats. However, one has to be very cautious with all such animals, particularly so whenever one is in their natural habitat.
Even though some people might wish to keep it as a companion animal, its wild nature prevents the domestication of Asian leopard cats. Other than that, depending on the country, it is unlawful to own a pet under most conservation laws.
The Asian leopard cat roams wild across the Asian continent, while breeders have developed the Bengal cat by outcrossing it with domestic cats. The physical features of Bengal cats remain very close to that of wild cats but the cats do not regress completely to their wild nature.
Asian leopard cats reign as keystone predators in their environments because of their ability to keep the numbers of their prey species in check. Often, they feed on small mammals and avians; thus, they contribute to the regulation of populations of these animals, which are either responsible for overgrazing or damaging plantations.
People can help in conserving Asian leopard cats by spreading information on the dangers that are besetting the species, supporting agencies that seek to protect the species and promoting policies that seek to change damaging circumstances to these cats.